The chip manufacturer is very proud of the efficiency of the Ryzen 9000, which will have more room for overclocking.
AMD has released more information about its next-generation Ryzen 9000 processors and the underlying Zen 5 CPU architecture. They repeated their claims about the excellent performance of the chip, which will be released at the end of July, that there will be a double-digit performance increase compared to the Zen 4 in both single- and multi-threaded tasks. However, AMD also boasted about the chips’ energy efficiency compared to Ryzen 7000, pointing out that they will reduce power consumption despite the performance increase.
AMD has lowered the default performance limits of three of the four Ryzen 9000 processors – the Ryzen 5 9600X, Ryzen 7 9700X and Ryzen 9 7900X – compared to the Ryzen 7000 versions of the same chips. Despite the lower default performance limit, all three mentioned chips still boast a double-digit performance improvement compared to their predecessors. According to AMD, the temperature of the Ryzen 9000 CPU will be up to 7 degrees Celsius cooler compared to the Ryzen 7000 chips at the same settings.
It’s worth noting that the increased TDP levels didn’t help performance much in the first place. The reduction of the TDP of the Ryzen 9000 is partly made possible by the architectural development. The Ryzen 9000’s TDP reduction could be made possible by a more modern manufacturing process, so AMD had some leeway to lower those power consumption numbers without affecting performance too much. TDP should be thought of as a performance limit rather than the actual amount of power used by the CPU for a given workload.
Still, AMD’s focus on power efficiency for the Ryzen 9000 series is commendable, especially since Intel’s high-end 13900K and 14900K processors suffered from crashes that appeared to be related to high power consumption and improper motherboard configurations. Intel hasn’t yet released a definitive statement on the cause of the problem, but it’s likely a side effect of pushing the chips’ thermal and electrical limits.
Ryzen 9000 CPUs can be overclocked by users who want to push those performance limits – AMD points out that each of the chips provides more leeway for automated overclocking with Precision Boost Overdrive, precisely because the default performance limits leave a little more power lying idle. . But as long as the chips perform well at their default settings, those who just want to build a PC without tinkering with it will be better off with chips that are cooler and use less power.

Another small but notable change in AMD’s slides, and good news for anyone who has already invested in a Socket AM5 motherboard or plans to in the near future: AMD has officially extended the socket’s guaranteed support period to at least 2027, and open leave the door open for subsequent support. That’s a two-year extension from the company’s “2025+” roadmap set at the end of 2022.
Of course, “support” can mean many different things. AMD still officially supports the AM4 socket for new CPUs and continues to rely on AM4 as a low-cost platform since the AM5 socket is still expensive. But these “new” releases were all repackages of various iterations of Ryzen 5000 CPUs from the late 2020s, rather than truly new products. Still, AMD’s official commitment to the longevity of the AM5 socket makes it easy for people who regularly upgrade their CPUs to recommend it.
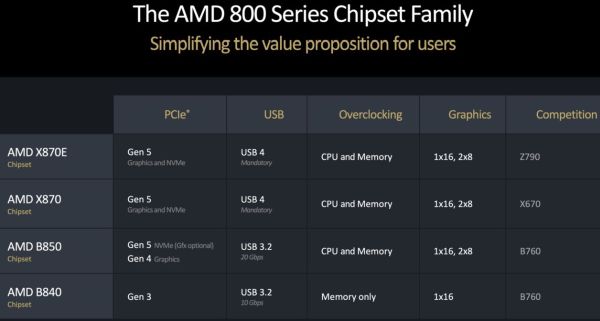
Ryzen 9000 chips can be inserted into any current AM5 motherboard after a BIOS update. The company will also bring out a range of 800-series chipsets for the new motherboards, though these will generally only feature minor improvements over the 600-series chipsets they replace. The X870E and X870 are guaranteed to have USB 4 ports, with the X870 supporting PCIe 5.0 speeds, while the X670 only supported PCIe 4.0 speeds for the GPU slot. The lower-end B850 chipset still supports PCIe 5.0 speeds for SSDs and PCIe 4.0 speeds for GPUs, while the even lower-end B840 chipset is limited to PCIe 3.0 speeds for all of these. The B840 also does not support CPU overclocking, although it can still overclock RAMs.
Source: sg.hu


