Autonomous robots controlled by artificial intelligence have offered a never-before-seen look inside a bee colony. They use cameras to closely monitor the queen and her retinue and generate large data sets for analyzing bee behavior. Scientists from the Artificial Intelligence Center of the Czech Technical University in Prague, together with colleagues from Austria, Great Britain and Turkey, have developed a breakthrough technology for researching the behavior of social insects.
Their autonomous robots, located in the honey bee research facility at the University of Graz, generate 1,400 GB of data every day. This data contains images of the queen bee and her interactions with the workers. Everything happens continuously in real time in high definition. The robotic system automatically analyzes the images and thus measures a number of parameters characterizing the activity of the queen and the health of the bee colony.
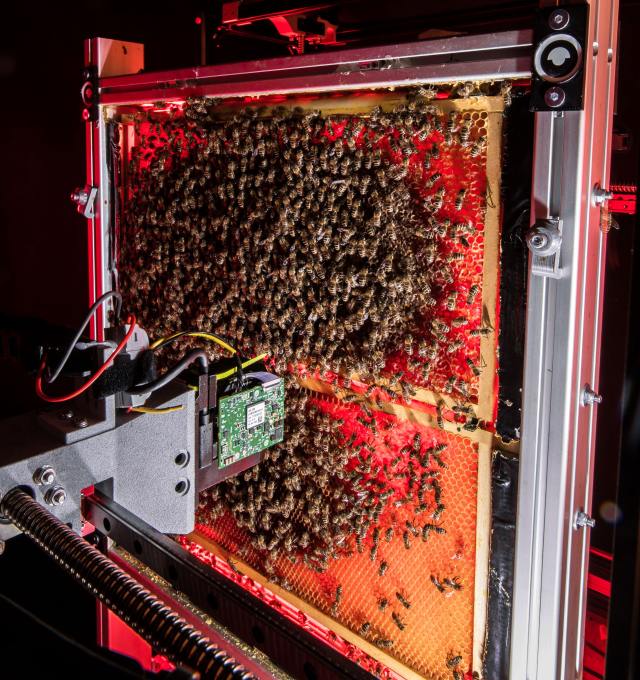 |
Image of the equipment used for the experiments. In the foreground is a robotic device with a camera head that continuously monitors the queen. Behind the hive is a second device. The robotic head automatically follows the queen and films her behavior. Since bees are blind to red light, these recordings are made in the infrared spectrum. |
In the new article “Autonomous tracking of honeybee behaviors over long-term periods with cooperating robots”, published in the renowned journal Science Robotics, Jiří Ulrich, a PhD student from the Center for Artificial Intelligence of the Faculty of Electrical Engineering at CTU, and his co-authors present the data that the robotic system collects. In addition to tracking the movements of the queen and workers, the robotic system also measures the total population of the hive and tracks the number of eggs laid.
For the first time, the new robotic system enabled such accurate, long-term and continuous collection of relevant data about a bee colony. The researchers demonstrate the versatility of this device using the example of 23 different parameters that the system can obtain from images, and emphasize that further analyzes will be added during the “RoboRoyale” project.
A scientific paper presents the first surprising findings about bee behavior. For example, the researchers found that the queen bee observed in this study covers a distance of about 1.5 kilometers per month (on two combs measuring approx. 42×33 cm), that she prefers to rest in certain places for up to 1.5 hours, and that even in the fading bee season in October lays an average of 187 eggs every day.
The robotic system was built around a fully functional bee colony in a so-called observation hive that allows the bees to behave naturally. The core of the system are two mobile camera heads that share the work autonomously (without commands from a human operator). When the queen walks, the robots move with her. When the queen moves to the other side of the comb, the robots work together to ensure her continuous monitoring. When the system judges that the queen is about to rest, the first camera continues to observe the bees nursing the queen, while the second camera performs a comb inspection to count the workers and take pictures of the comb.
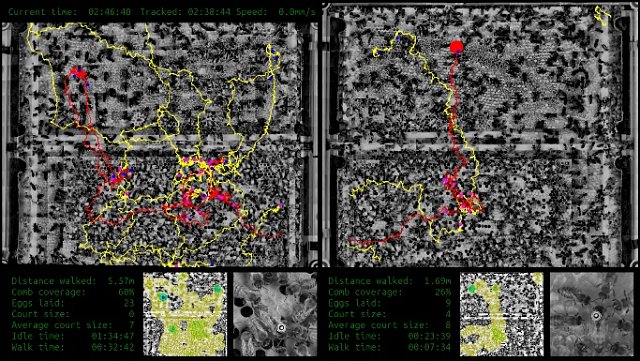 |
System dashboard showing two sides of the observation hive. The current trajectory of the queen is in red, the past trajectory in yellow. The positions of the loaded eggs are marked with purple dots. At the bottom is information about the activity of the queen and her court. |
The cameras use infrared light to avoid affecting the behavior of the bees, as they are blind to red light. The high-resolution recordings are then analyzed using advanced computer vision methods. During the one month study, the system processed more than 100 million images. This quantity is virtually impossible to analyze by hand.
An international team composed of researchers from FEL CTU, Durham University, University of Graz and Middle East Technical University in Ankara showed that intelligent robots are changing the rules of the game in research on insect behavior and ecology.
Published article
Ulrich et al. (2024) „Autonomous tracking of honeybee behaviors over long-term periods with cooperating robots“, Science Robotics.
Project team and project information:
- H2020 FET-OPEN project “RoboRoyale” (duration: November 2021 – October 2026)
- Project website: roboroyale.eu
Project partners:
- Farshad Arvin, University of Durham, Durham, Great Britain.
- Thomas Schmickl, Universität Graz, Austria,
- Tomáš Krajník, Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic
- Erol Sahin, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey
Source: www.cad.cz


